Last Updated on April 30, 2024
Day trading and position trading are popular approaches, offering different paths to profit, each with its own appeal and risks. Traders need to consider the pros and cons of these methodologies to make an informed choice about which fits their profile better.
This article provides guidance on navigating the world of day and position trading to help you find the trading style that you are more likely to succeed with.
What is Day Trading?
As the name implies, day trading is the process of buying and selling financial instruments, like stocks, currencies, or commodities, within a single trading day. This approach is characterized by its short-term nature, with traders closing their positions before the day ends.
The goal of a day trader is to capitalize on intraday price fluctuations. Day traders typically prefer highly liquid markets, such as futures, forex, and derivatives, to avoid being locked in a position at day’s end. By closing their positions at the end of the day, traders can cut their exposure to overnight volatility risks.
Day traders rely on technical analysis tools and indicators to spot short-term opportunities and make quick trading decisions.
Scalping is an example of a day trading strategy. It involves making multiple quick trades throughout the day to capture small price movements. Scalpers leverage high trading volumes to amplify the small gains from each trade.
What is Position Trading?
Position trading involves holding positions for an extended period, ranging from weeks to months or even years, to ride larger market trends. This long-term strategy enables traders to profit from broader market movements and avoid short-term volatility.
Position traders seek to benefit from more significant price changes over the long term. They prefer trading instruments that offer liquidity, stability, and the potential for sustained price movements, including stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and commodities.
Fundamental analysis, along with macroeconomic trend and geopolitical event monitoring, plays a significant role in the trading decisions of position traders. They may also employ specific technical analysis tools like trend lines, patterns, and moving averages to identify and confirm trends.
Trend following is an example of a position trading strategy. Traders identify and ride significant trends in the market, entering positions aligned with the prevailing trend and staying in until clear signs of a trend reversal emerge.
Day Trading vs Position Trading
Understanding the key differences between day trading and position trading is crucial for aligning your trading strategy with your goals, risk tolerance, and time commitment.
Here are some important factors to consider:
Trading Style
Day trading and position trading differ significantly regarding trading style, with each strategy requiring unique trading characteristics.
Day trading demands strong focus and discipline. The ability to make quick decisions in a fast-paced environment is of crucial importance. As a day trader, you must remain vigilant and informed about prevailing market movements to swiftly react to short-term price fluctuations.
The dynamic nature of day trading can be demanding, so it’s essential to be prepared to handle emotional pressure. Day traders must maintain discipline and adhere to their trading plans, keeping fear and greed in check. Avoid making impulsive or irrational trading decisions.
On the other hand, position trading suits a more patient and long-term-oriented trader profile. As a position trader, you can adopt a more relaxed trading approach. Holding positions for months or even longer means you’re less concerned about short-term price fluctuations.
However, position trading also involves emotional pressure, albeit of a different nature. It requires emotional discipline to remain unaffected and maintain focus on the bigger picture, even during short-term market fluctuations.
Required Trading Skills
The trading skills required for day trading differ significantly from those needed for position trading.
Day traders heavily rely on technical analysis to identify short-term price patterns, trends, and entry/exit points. While you don’t necessarily need to be an expert financial analyst, having a good understanding of basics such as chart patterns, support/resistance levels, moving averages, and more is important.
On the other hand, position traders primarily rely on fundamental analysis to evaluate the long-term growth prospects of assets. Proficiency in analyzing company financials is essential, including profitability, P/E ratio, cash flow, insolvency risk, and other company fundamentals. Position traders should also consider industry trends and macroeconomic factors. The goal is to utilize these indicators to identify undervalued assets with long-term growth potential.
Risk
Both day trading and position trading involve some degree of risk. However, day trading is generally considered riskier than position trading due to certain factors:
- Time Horizon: Day traders make trading decisions within short time frames, executing trades within a single trading day. This exposes them to higher levels of volatility and rapid price fluctuations.
- Trading Frequency: Day trading often involves a high frequency of trades throughout the day to take advantage of intraday market volatility. The more trades executed, the higher the transaction costs and potential slippage, which can reduce profits.
- Emotional Pressure: The fast-paced nature of day trading can create emotional pressure, leading to impulsive decision-making and psychological biases.
However, position trading also carries risks, including:
- Premature Exit: There is a tendency to exit positions prematurely based on short-term market movements. This could happen due to emotions or the incorrect belief that the fundamentals aren’t as good as previously thought.
- External Events: Market trends can be interrupted abruptly due to external issues, as seen with the sudden impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on the previously steady climb of the U.S. stock market. Here’s an illustration:
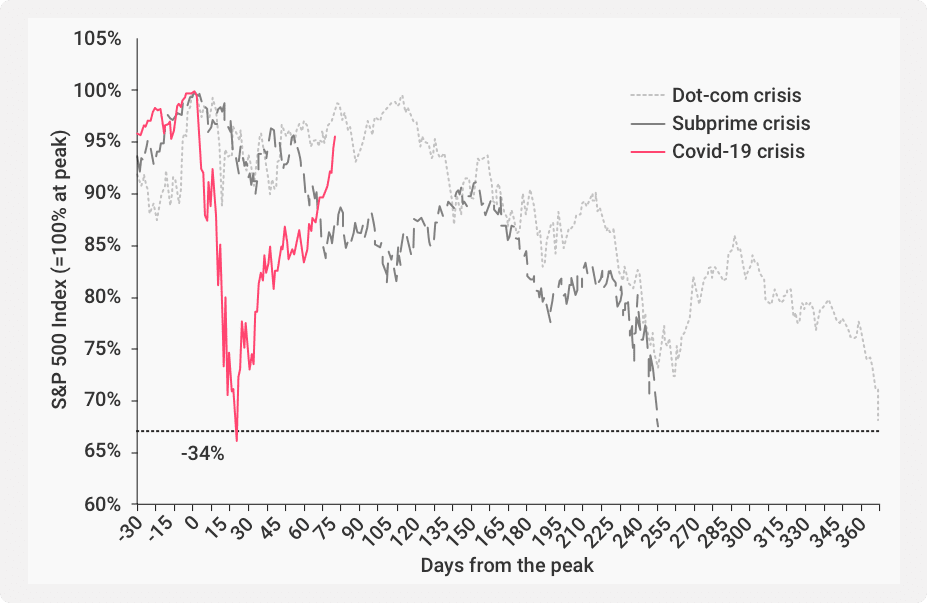
When news of the pandemic hit, the bullish market trend just suddenly reversed, leaving positional traders with huge losses.
Profit Opportunities
Day traders typically execute more trades, seeking smaller but more frequent gains. Their main objective is to capitalize on intraday volatility and profit from favorable price movements.
On a side note, did you know that it is possible to start day trading with as little as $500?
Successful day traders implement strict risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and managing position sizes, to safeguard their capital.
On the other hand, position traders aim to profit from significant price movements or appreciation that occur over a longer timeframe. By riding market trends, they have the potential to capture substantial profits.
Position trading also offers the benefit of diversification. Unlike day traders who focus on intraday trading, position traders can open positions across multiple markets and asset classes.
For example, position traders can construct a well-diversified portfolio comprising equities, bonds, commodities, real estate, currencies, cryptocurrencies, and other alternative investments. This diversification helps mitigate risk and provides exposure to broad profit opportunities across different asset classes. As a result, position traders generally achieve higher risk-adjusted returns compared to day traders.
The Sharpe, Sortino, and Treynor ratios are notable risk-reward ratios used for evaluating investments based on their risk/reward. A higher value indicates that, for a given level of risk, the return is higher.
Time Commitment
Generally speaking, day trading requires a more significant time commitment than position trading.
Due to the short-term focus of day trading, traders have to be actively tuned in to market activity during trading hours. They also spend time executing trades, adjusting stop-loss levels, and managing positions throughout the trading day.
In contrast, position traders tend to be more patient and focused on long-term growth. This means they don’t have to actively monitor the market or make quickfire adjustments to their positions based on short-term price actions.
Tips for Choosing Between Day Trading and Position Trading
- Clearly define your trading goals: Are you seeking short-term profits from rapid price movements, or are you looking for long-term appreciation by capturing extended trends?
- Assess your time availability: Evaluate the amount of time you can dedicate to trading. Consider your other commitments, work schedule, and personal activities to determine which trading style aligns with the time you have available.
- Evaluate your risk tolerance: Think about the amount of risk that you are willing to accept as a trader and choose the trading style that best suits it.
- Start small: Whether day or position trading, only trade with what you can afford to lose. Starting with limited capital helps you gauge your comfort level with the chosen style before committing more significant amounts.
- Consider your trading skills and preferences: Assess your skill set and preferences to choose the trading strategy that aligns with your strengths and interests.
- Commit to continuous learning: Day trading and position trading aren’t mutually exclusive. There’s no reason why you can’t learn both and utilize them based on the situation.
Conclusion
Day trading and position trading are two distinct trading styles that differ in terms of required trading skills, levels of risk, profit opportunities, and time commitment.
Ultimately, it is essential to align the chosen trading style with your goals, risk tolerance, and available resources.
However, always remember that both day and position trading can be profitable, provided you approach them with the proper mindset and discipline.